Introduction: How CI/CD Pipeline Works in Modern Software Development
In today’s fast‑paced software world, understanding how CI/CD pipeline works is essential for developers, DevOps engineers, and even tech content creators. CI/CD pipelines help teams deliver software faster, with fewer errors, and in a fully automated way. Instead of manually building, testing, and deploying applications, CI/CD automates everything from code integration to production release. This article explains how CI/CD pipeline works step by step, using simple language, real‑world examples, and best practices so beginners can easily understand the full process.
What is a CI/CD Pipeline?
A CI/CD pipeline is an automated workflow that helps software teams build, test, and deploy code continuously. It ensures that new code changes are safe, tested, and ready for users.
CI – Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration focuses on frequent code integration into a shared repository.
Key goals of CI:
- Detect bugs early
- Improve code quality
- Reduce integration issues
CD – Continuous Delivery vs Continuous Deployment
CD can mean two things:
- Continuous Delivery – Code is always ready for release, but deployment may need manual approval.
- Continuous Deployment – Code is automatically deployed to production without manual intervention.
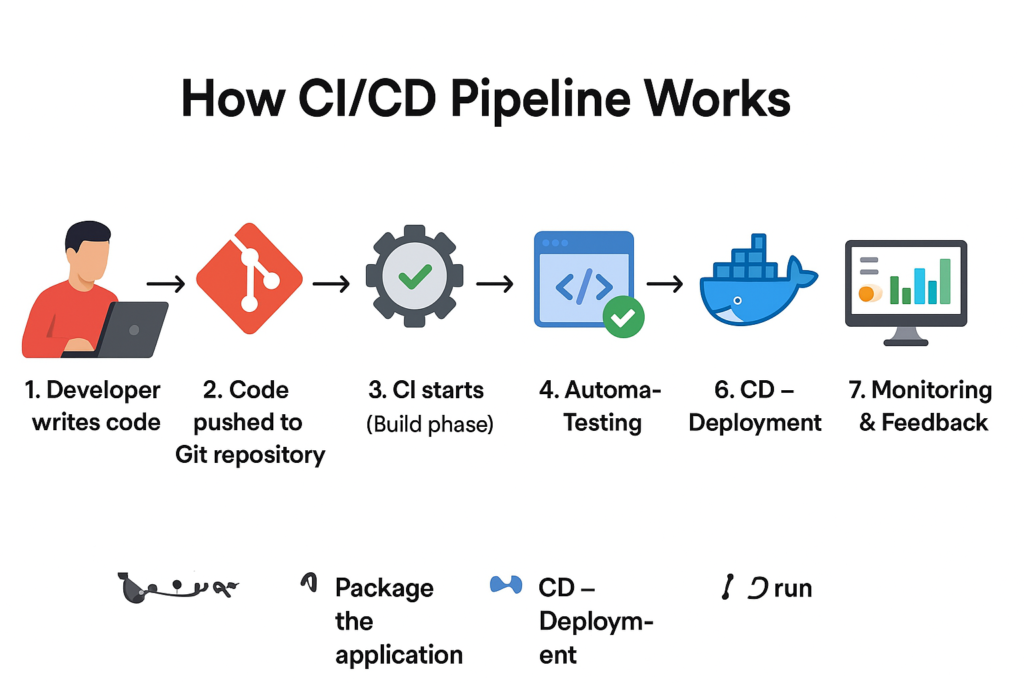
How CI/CD Pipeline Works: Step‑by‑Step Explanation
Step 1: Code Development
Developers write code on their local machines and work on features, bug fixes, or improvements.
Best practices:
- Use feature branches
- Write clean, readable code
- Follow coding standards
Step 2: Code Push to Version Control System
Once the code is ready, it is pushed to a version control system like Git.
Popular platforms:
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Bitbucket
This push automatically triggers the CI/CD pipeline.
Step 3: Build Process (CI Stage)
The pipeline starts by building the application.
Build activities include:
- Installing dependencies
- Compiling code
- Creating artifacts or Docker images
If the build fails, the pipeline stops immediately.
Step 4: Automated Testing
Automated tests ensure that the code works correctly.
Types of tests:
- Unit tests
- Integration tests
- Functional tests
- Security tests
Only when all tests pass does the pipeline move forward.
Step 5: Code Quality & Security Checks
Modern CI/CD pipelines include quality and security scans.
Checks may include:
- Code linting
- Vulnerability scanning
- Dependency checks
This step improves application reliability and security.
Step 6: Artifact Packaging
After successful testing, the application is packaged.
Common formats:
- Docker images
- JAR / WAR files
- ZIP packages
These artifacts are stored in repositories for deployment.
Step 7: Deployment (CD Stage)
The application is deployed to environments such as:
- Development
- Staging
- Production
Deployment can be:
- Manual approval based (Continuous Delivery)
- Fully automated (Continuous Deployment)
Step 8: Monitoring & Feedback
Once deployed, monitoring tools track performance and errors.
Monitoring includes:
- Logs
- Error alerts
- Performance metrics
Feedback helps teams fix issues quickly.
CI/CD Pipeline Flow Diagram (Conceptual)
Code → Git Push → Build → Test → Package → Deploy → Monitor
CI/CD Pipeline Commands Example (Real Practical Commands)
Understanding how CI/CD pipeline works becomes much easier when you see real commands used in pipelines. Below are commonly used commands at each stage.
Git Commands (Source Code Management)
These commands are used by developers and CI tools to manage code:
git clone https://github.com/username/project.git
git status, git add, git commit -m “Feature added”,git push origin main
Popular CI/CD Tools
CI Tools
- Jenkins
- GitHub Actions
- GitLab CI/CD
- CircleCI
CD & Deployment Tools
- Docker
- Kubernetes
- Argo CD
- AWS CodePipeline
Real‑World Example: How CI/CD Pipeline Works in a Web App
Imagine updating a company website:
- Developer updates code
- Pushes to GitHub
- Pipeline builds the app
- Tests run automatically
- App deploys to server
- Users see changes instantly
No manual deployment required.
Benefits of CI/CD Pipeline
- Faster software delivery
- Reduced human errors
- Early bug detection
- Improved collaboration
- Better user experience
Common CI/CD Pipeline Challenges
- Poor test coverage
- Slow build times
- Security misconfigurations
- Lack of monitoring
Solution: Proper planning and tool selection.
Best Practices for CI/CD Pipelines
- Keep pipelines fast
- Automate everything
- Use version control properly
- Secure secrets and credentials
- Monitor continuously
Internal & External Resources
Internal Links (Example):
- DevOps Basics Guide
- Docker for Beginners
- Jenkins Tutorial for Beginners
External Links (Trusted Sources):
- Official Jenkins Documentation
- Docker Official Website
- Kubernetes Documentation
Conclusion: Why CI/CD Pipeline is the Future
Understanding how CI/CD pipeline works is crucial for modern software development. It enables faster releases, better quality, and reliable deployments. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, mastering CI/CD will improve productivity and career growth. As technology evolves, CI/CD pipelines will continue to be the backbone of DevOps and cloud‑native applications.