In today’s fast-paced software development world, Jenkins CI/CD Tool has become one of the most important automation platforms for DevOps engineers. Jenkins CI/CD Tool helps teams automate building, testing, and deploying applications efficiently. Whether you are a beginner in DevOps or an experienced developer, understanding Jenkins CI/CD Tool can significantly improve your workflow and productivity.
Jenkins enables Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD), making software releases faster, more reliable, and error-free. In this complete guide, we will explore everything about Jenkins — features, installation, benefits, architecture, plugins, and real-world usage.
What is Jenkins?
Jenkins is an open-source automation server used to automate software development processes like building, testing, and deployment.
It was originally developed as Hudson in 2004 and later renamed Jenkins. Today, it is one of the most widely used CI/CD tools in DevOps.
Why Jenkins is Popular?
- Open-source and free
- Large plugin ecosystem (1800+ plugins)
- Platform independent (Windows, Linux, macOS)
- Strong community support
- Easy integration with tools like Git, Docker, Kubernetes
What is CI/CD in DevOps?
Before understanding Jenkins deeper, let’s quickly understand CI/CD.
Continuous Integration (CI)
CI means developers regularly merge their code changes into a central repository. Automated builds and tests run to detect errors early.
Continuous Delivery (CD)
CD ensures that code changes are automatically prepared for release to production.
Learn more about DevOps principles from:
🔗 https://aws.amazon.com/devops/what-is-devops/ (External Trusted Link – AWS)
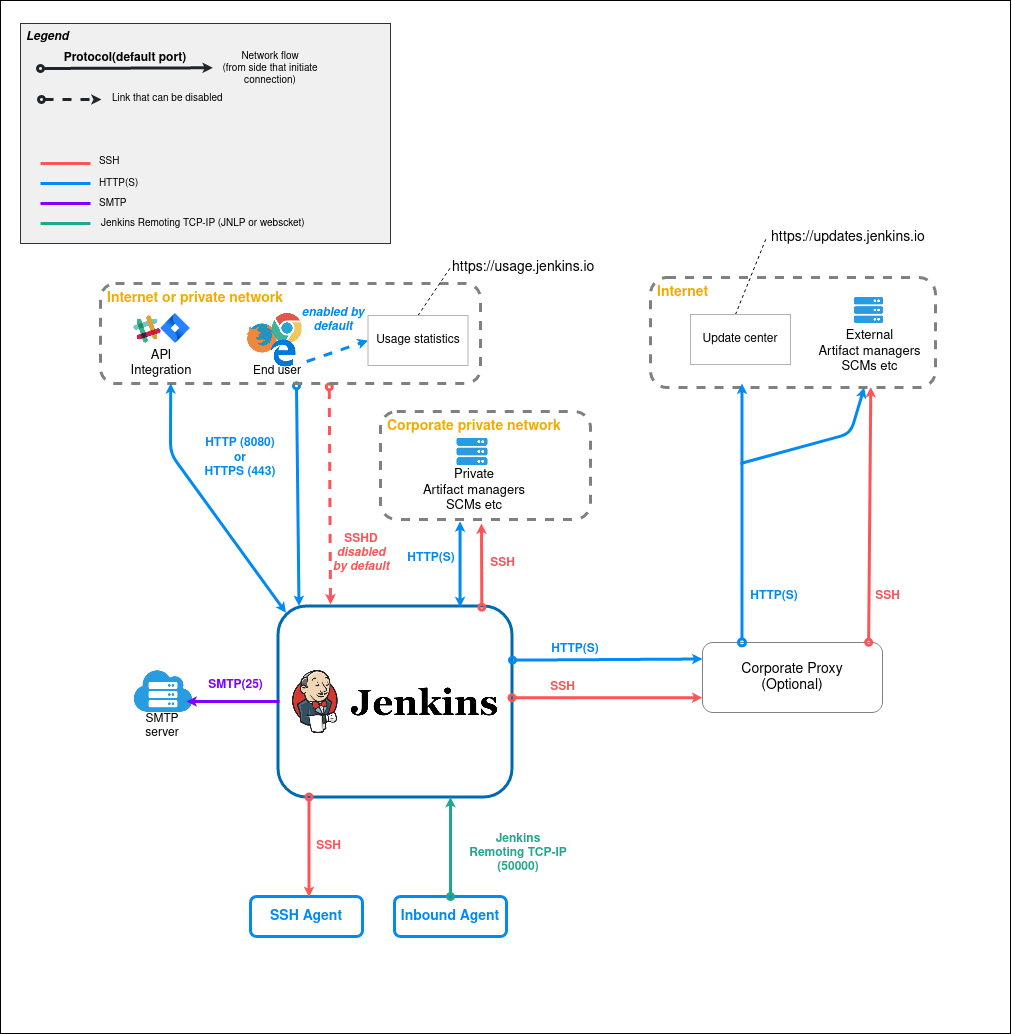
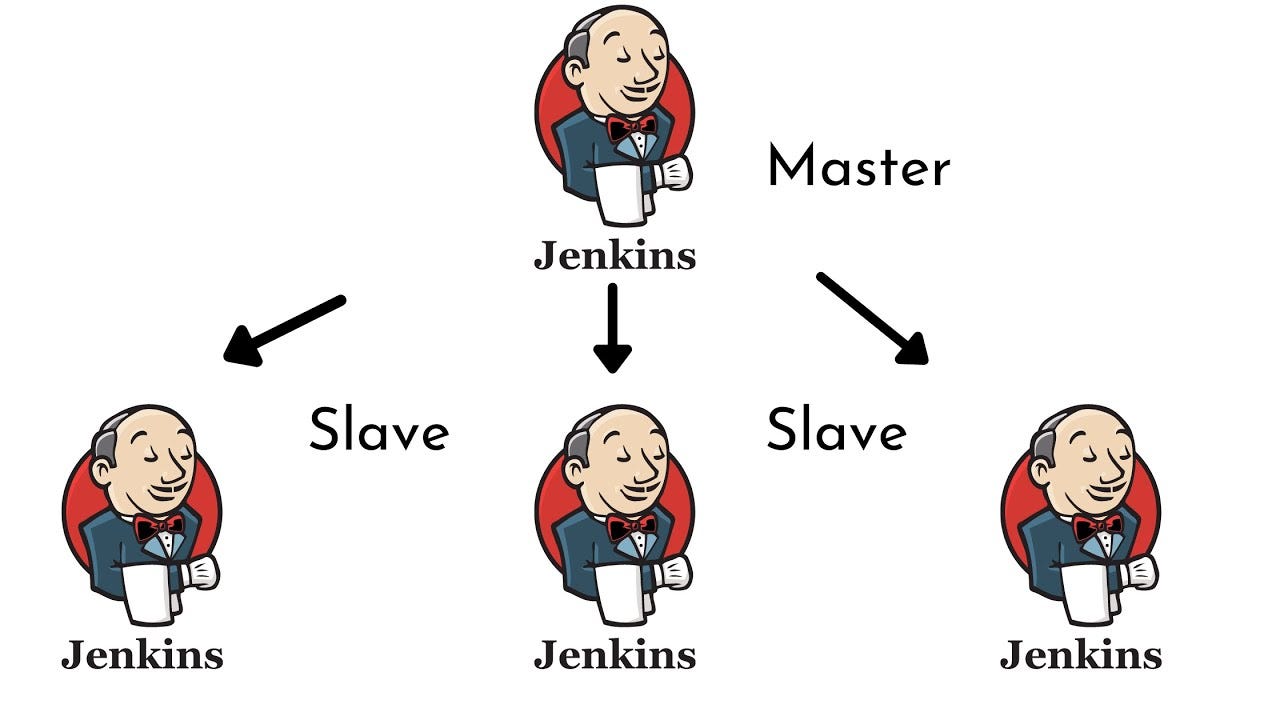
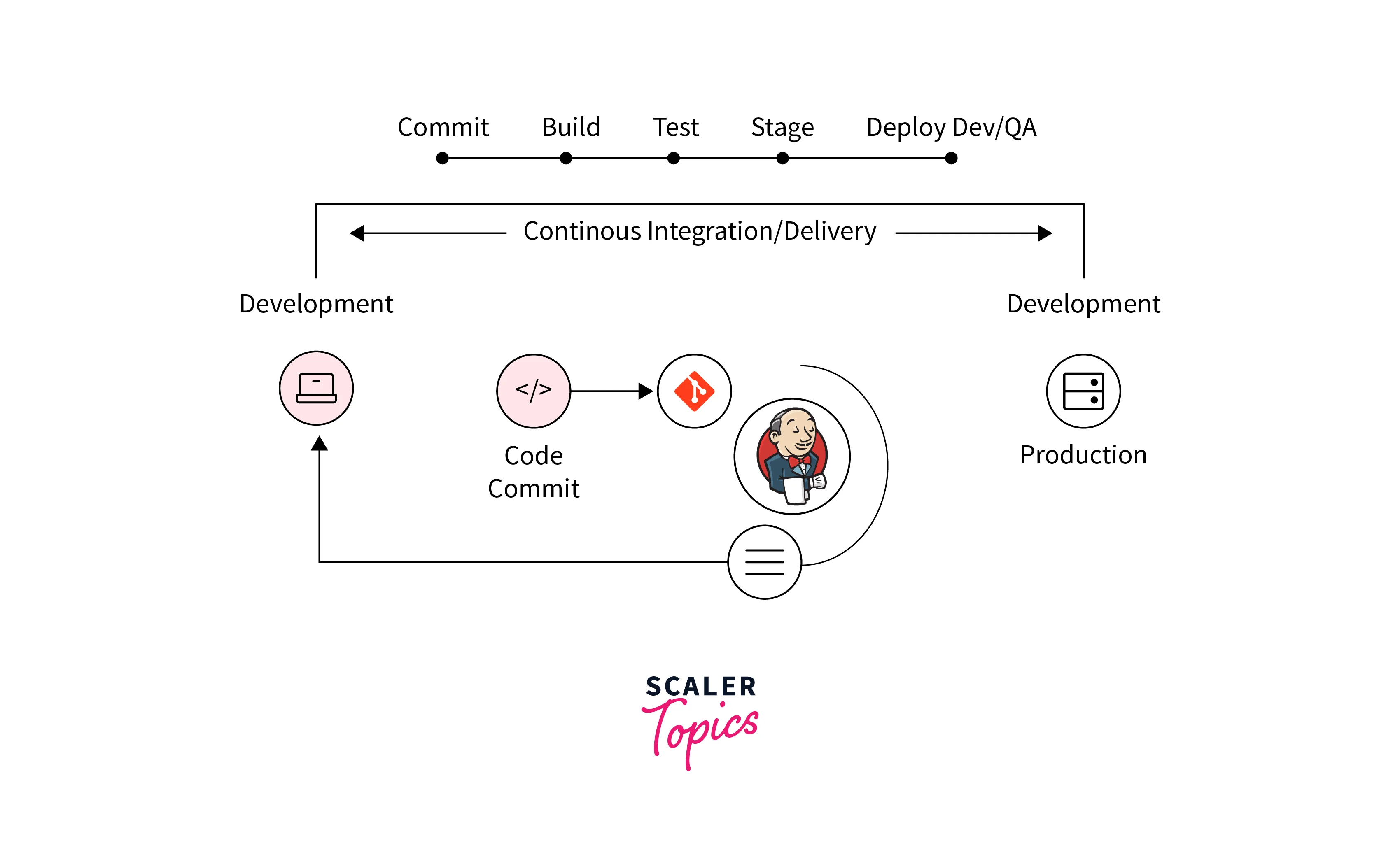
How Jenkins Works?
4
Jenkins works using a Master-Agent architecture.
1. Jenkins Master
The master node:
- Schedules jobs
- Monitors builds
- Assigns tasks to agents
2. Jenkins Agent (Slave)
Agents:
- Execute build tasks
- Run tests
- Deploy applications
Key Features of Jenkins CI/CD Tool
1. Pipeline as Code
Jenkins allows defining pipelines using a Jenkinsfile.
2. Plugin Support
Jenkins supports integration with:
- Git
- Docker
- Kubernetes
- Maven
- Gradle
- AWS
3. Distributed Builds
You can run builds across multiple machines.
4. Easy Configuration
Web-based UI makes configuration simple.
Jenkins Installation Guide (Beginner Friendly)
Step 1: Install Java
Jenkins requires Java (JDK 11 or later).
Step 2: Download Jenkins
Official Website:
🔗 https://www.jenkins.io/
Step 3: Run Jenkins
After installation:
- Access Jenkins at:
http://localhost:8080 - Enter admin password
- Install suggested plugins
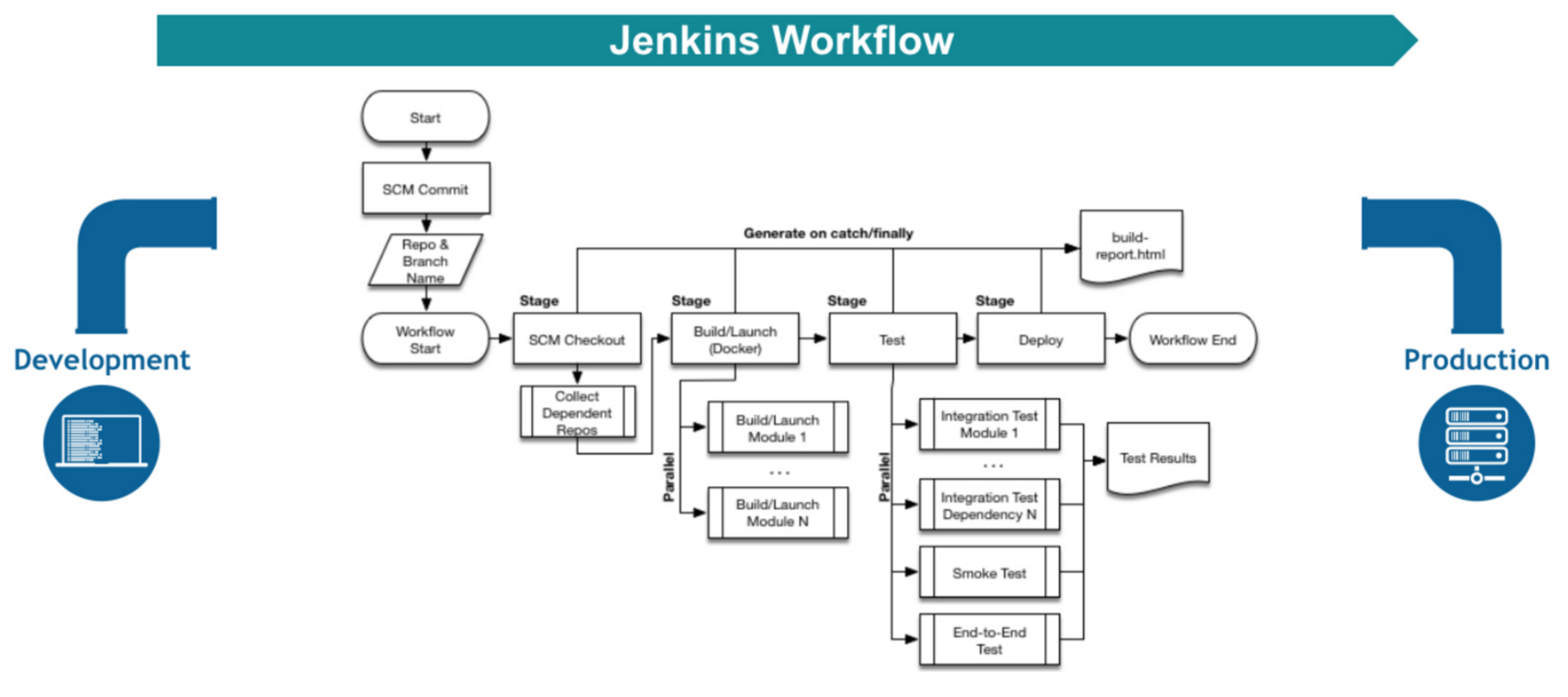
Jenkins Pipeline Explained

4
Jenkins Pipeline is used to automate CI/CD workflow.
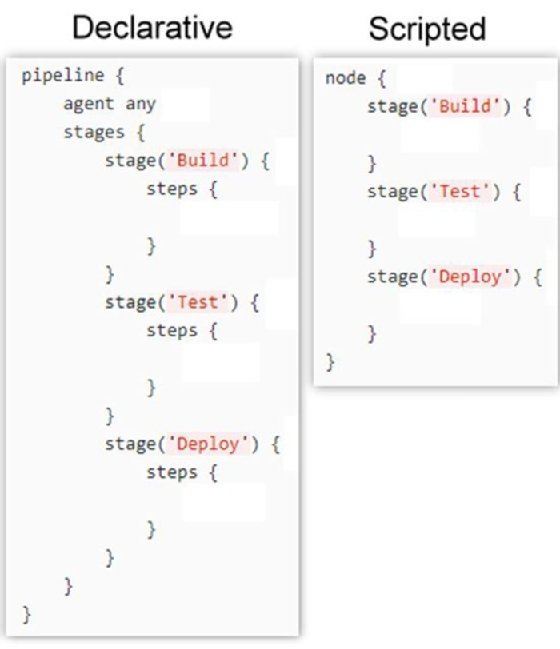
Types of Pipelines
1. Declarative Pipeline
- Simple syntax
- Recommended for beginners
2. Scripted Pipeline
- More flexible
- Uses Groovy scripting
Example Jenkinsfile:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
echo 'Building...'
}
}
stage('Test') {
steps {
echo 'Testing...'
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
echo 'Deploying...'
}
}
}
}
Advantages of Using Jenkins
1. Cost Effective
Open-source and free to use.
2. Faster Development
Automates repetitive tasks.
3. Early Bug Detection
CI catches errors early.
4. Scalability
Can handle large enterprise projects.
Jenkins vs Other CI/CD Tools
| Feature | Jenkins | GitHub Actions | GitLab CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Source | Yes | Limited | Yes |
| Plugins | 1800+ | Limited | Moderate |
| Customization | High | Medium | Medium |
| Community | Very Large | Growing | Large |
Common Jenkins Plugins
Some popular plugins include:
- Git Plugin
- Docker Plugin
- Kubernetes Plugin
- Pipeline Plugin
- Blue Ocean Plugin
Best Practices for Jenkins CI/CD
Keep Jenkins Updated
Backup Jenkins Data
Use Pipeline as Code
Monitor Build Performance
Secure Jenkins with Authentication
Security documentation:
🔗 https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/security/
Real-World Use Case of Jenkins
Example workflow:
- Developer pushes code to GitHub
- Jenkins triggers automatically
- Runs build and tests
- Creates Docker image
- Deploys to Kubernetes
Companies using Jenkins:
- Netflix
- eBay
Internal Linking Example (For Your Blog)
You can add internal links like:
- Read our guide on What is DevOps and How It Works
- Learn about Docker Complete Tutorial for Beginners
- Kubernetes Beginner Guide
(Replace with your actual blog URLs.)
Challenges of Jenkins
- Complex configuration for beginners
- Plugin dependency issues
- Requires maintenance
Future of Jenkins
Even though newer tools like GitHub Actions are growing, Jenkins still dominates enterprise environments due to:
- Flexibility
- Plugin ecosystem
- Large community support
Conclusion
The Jenkins CI/CD Tool remains one of the most powerful and reliable automation tools in DevOps. From continuous integration to automated deployment, Jenkins helps teams deliver software faster and more efficiently. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced DevOps engineer, learning Jenkins can significantly boost your career.
With its massive plugin ecosystem, scalability, and flexibility, Jenkins continues to be a top choice for CI/CD implementation and beyond.
If you are serious about mastering DevOps, Jenkins is a must-learn tool.